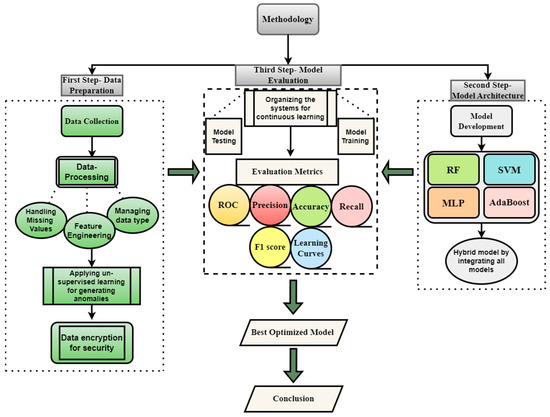
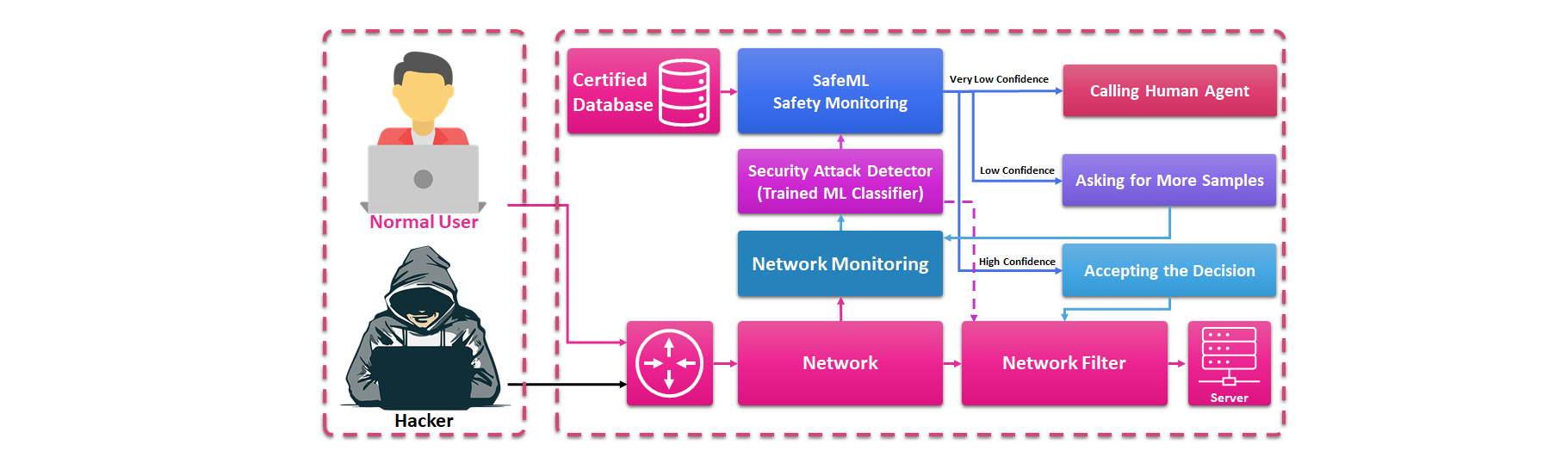
Methodology
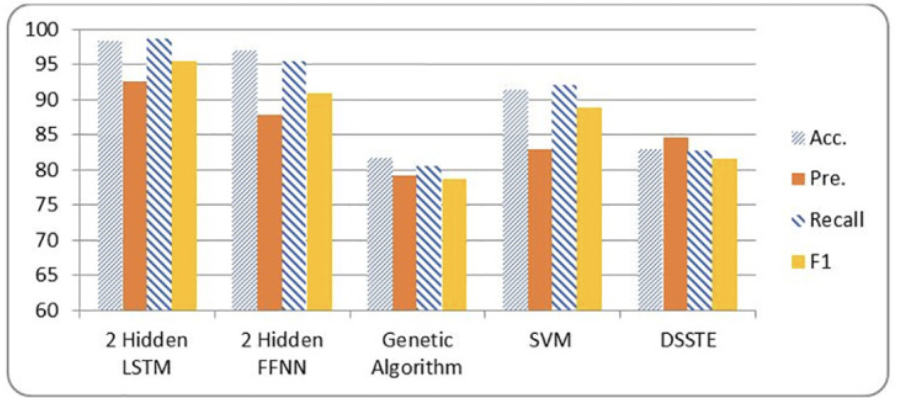
Our approach involves a comparative study of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, and Random Forest classifiers. Each model was trained on the CICIDS2017 dataset, a comprehensive benchmark dataset for intrusion detection. We preprocessed the data by removing null values, encoding categorical features, and standardizing numerical inputs before training. Each model was evaluated using accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and false positive rate.